Python Introduction
Python is a general-purpose interpreted, interactive, object-oriented and high-level programming language. Python was developed by Guido Van Rossum in 1989 while working at National Research Institute in the Netherlands.
Where can we use Python?
For Desktop Application
For Web Application
For Database Application
For Network Programming
Machine Learning etc.,
Python Installation
How To Install Python on Windows?
Visit the Python official website https://www.python.org/downloads/
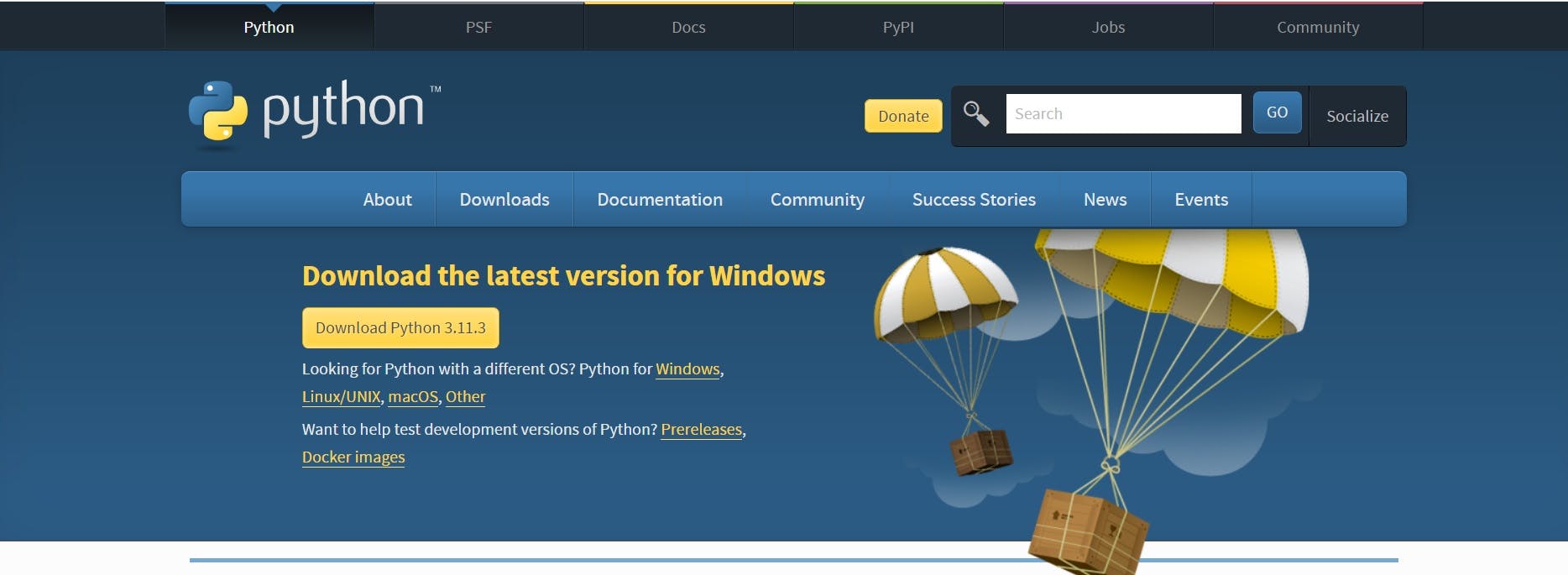
Click on the Download Python button. It will download the .exe file on your machine.
Click on the executable file and install Python.
Once the installation is finished check whether Python is installed or not by typing this command: python --version
How To Install Python on Ubuntu?
1. Update the os.
sudo apt update
2. Download the latest Python version
sudo apt install python3
3. Now check Python Version
python3 --version
Python Variables
Variable means storing a value on a reserved memory location.
How to declare a variable?
e.g.
a=5 <= Declare a variable here the value is in integer form
print(a) <=print is an inbuilt function in Python to give output.
Python Data Types
Datatype represents the type of data present inside a variable. Python contains the following data types:
Numbers (int, float, complex)
a. int: int represents the whole number.
e.g. a=10 <= Integer value
print(a) <= It will print output
print(type(a)) <= It will show the type of variable

b. float: It is used to represent values in decimal values.
e.g. b=2.545 <= Floating value
print(b) <= It will print output
print(type(b)) <= It will show the type of variable

c. Complex:
e.g. c=4+7j <= 4 is a Real part and 7j is a imaginary part.
print(c) <= It will print output
print(type(c)) <= It will show the type of variable

String
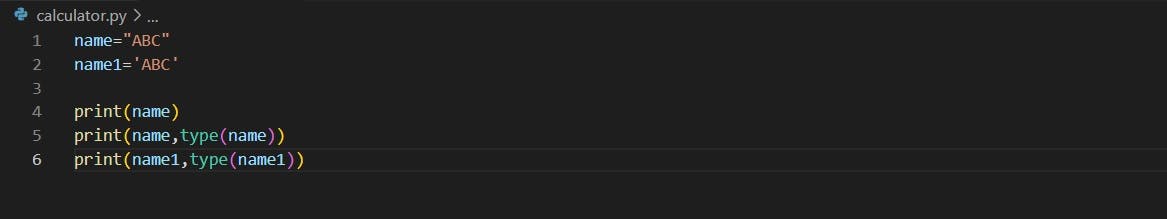
The string represents a sequence of characters closed with double quotes(") or single quotes(').
e.g. name="ABC" or name1='ABC'
print(name)
print(name,type(name))
print(name1,type(name1))

Boolean
This data type is used to represent boolean values in True or False. Only True and False value is allowed for this data type. Do not use double quotes (") or single quotes (') before and after.
e.g. a=True or b=False
print(a,type(a))
print(b,type(b))


Data conversion
In Python data conversion is possible.
e.g. num1=10
num2=float(num1)
print(num2)

Sequenced Data type (list, Tuple, Range, data dictionary, set)
a.list:
The list is an ordered collection of data with elements separated by a comma and enclosed within square brackets. lists are mutable and can be edited after creation.
e.g.
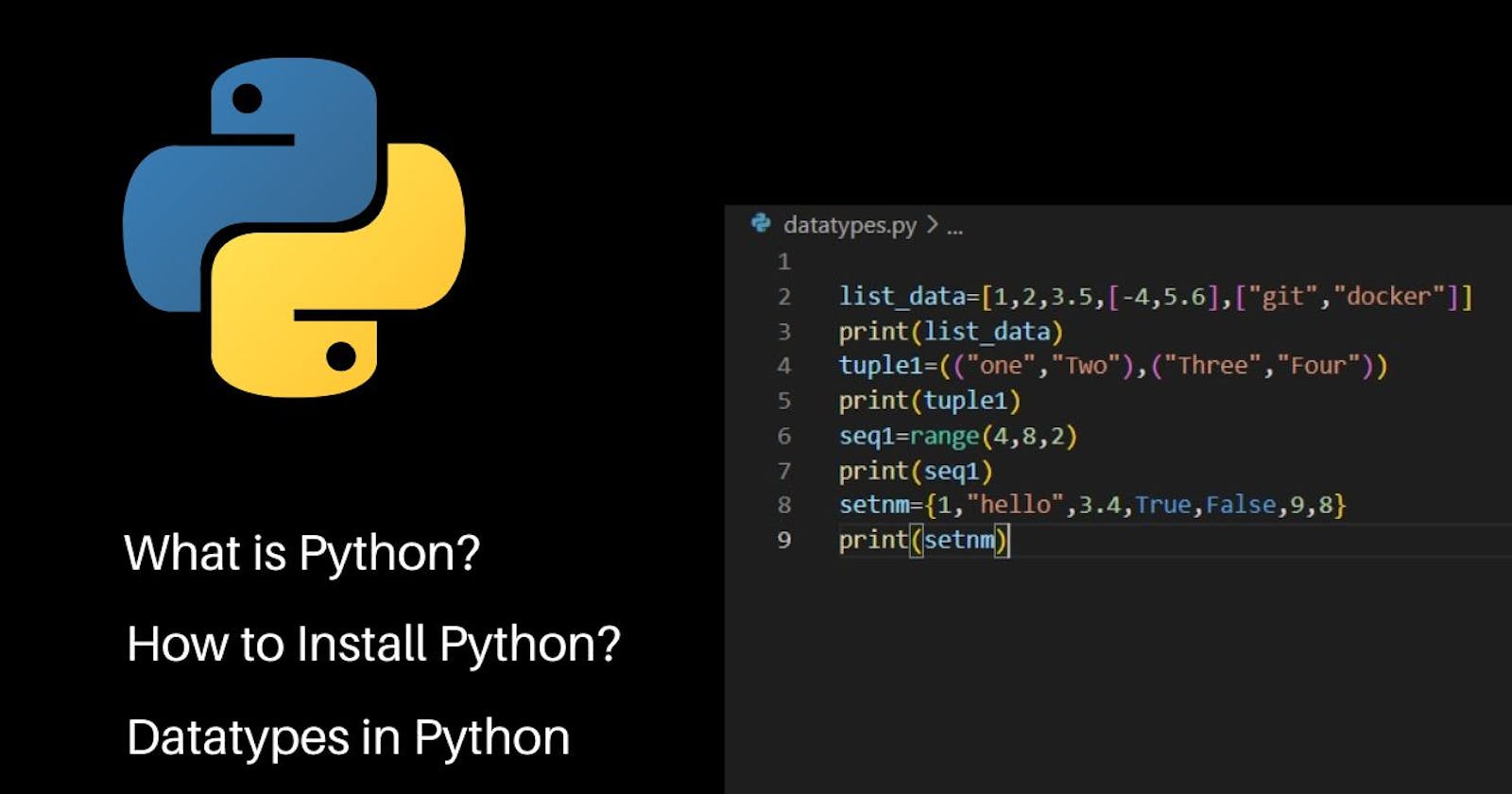
list_data=[1,2,3.5,[-4,5.6],["git","docker"]] print(list_data)
b.Tuple
A Tuple is an ordered collection of data with elements separated by a comma and enclosed within Parenthesis. Tuples are immutable and can be edited after creation.
tuple1=(("one","Two"),("Three","Four")) print(tuple1)
c.Range
It returns a sequence of numbers that is specified by the user. If it is not specified by the user then it will start with 0 and increment it by 1.
seq1=range(10) print(seq1)
d.data dictionary:
It is an ordered collection of data in a Key: value pair. Key: value pair enclosed with curly braces {}.
dictname={"server":"webserver","provider":"AWS"} print(dictname)
e.set:
It is an unordered collection of elements in which no elements are repeated and they store multiple values in a single variable.
setnm={1,"hello",3.4,True,False,9,8} print(setnm)
Thank you for reading this blog.Happy Learning!!!!!
You can follow me on LinkedIn for my daily updates:- linkedin.com/in/parimal-pradhan-b62021168
Great initiative by the #trainwithshubham community. Thank you Shubham Londhe